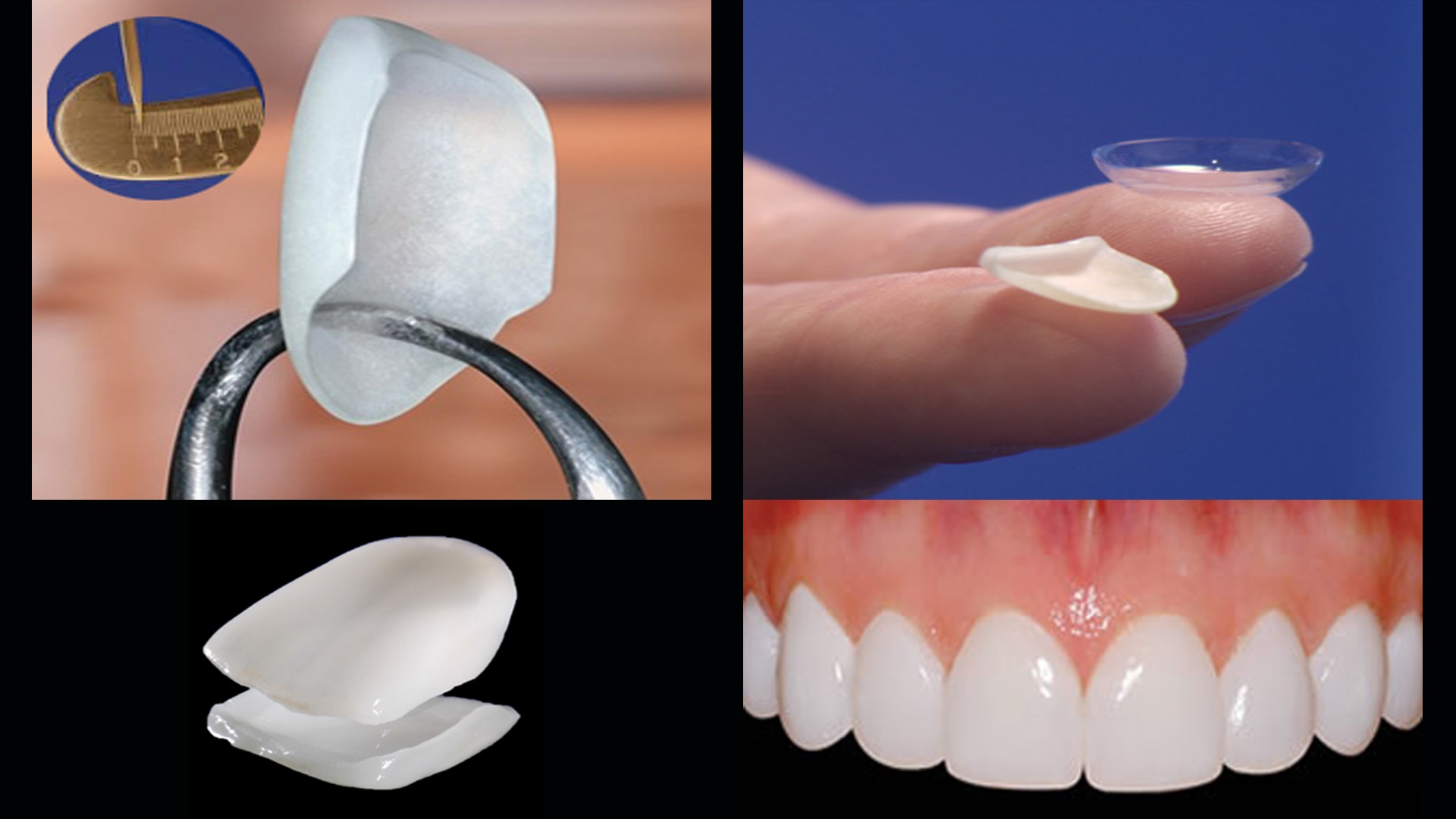
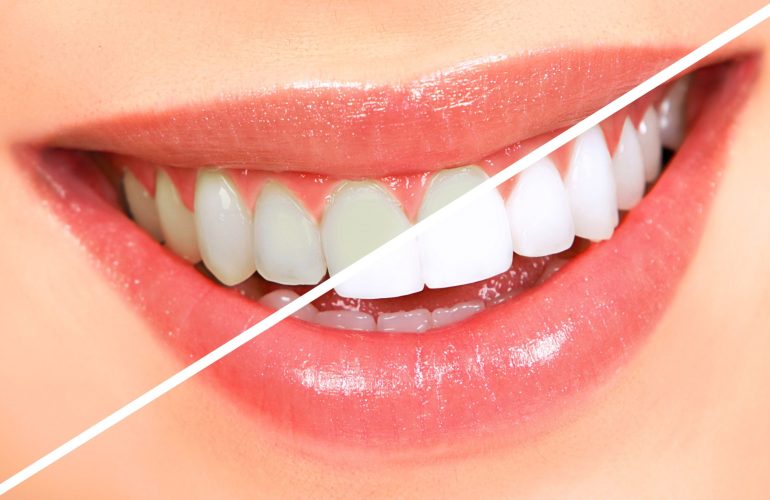
What are Dental Veneers?
Dental veneers (sometimes called porcelain veneers or dental porcelain laminates) are wafer-thin, custom-made shells of tooth-colored materials designed to cover the front surface of teeth to improve your appearance. These shells are bonded to the front of the teeth changing their color, shape, size, or length.
Dental Veneer Benefits
Veneers offer these advantages:
-
They provide a natural tooth appearance.
-
Gums tolerates porcelain well.
-
Porcelain veneers are stain resistant.
-
A color can be selected to make dark teeth appear whiter.
-
They generally don’t require as much shaping as crowns do, yet they are stronger and look better.
Dental Veneer Risks
Downsides to dental veneers include:
-
The process cannot be undone.
-
Veneers cost more than composite resin bonding.
-
Veneers usually cannot be repaired if they chip or crack.
-
Because enamel has been removed, your tooth may become more sensitive to hot and cold foods and drinks.
-
Veneers may not exactly match the color of your other teeth. Also, the veneer’s color cannot be altered once it’s in place. If you plan on whitening your teeth, you need to do so before getting veneers.
-
Though not likely, veneers can dislodge and fall off. To minimize the chance of this occurring, do not bite your nails, chew on pencils, ice or other hard objects, or otherwise put too much pressure on your teeth.
-
Teeth with veneers can still experience decay, possibly necessitating full coverage of the tooth with a crown.
-
Veneers are not a good choice for people with unhealthy teeth (for example, those with decay or active gum disease), weakened teeth (as a result of decay, fracture, large dental fillings), or for those who don’t have enough existing enamel on the tooth surface.
-
People who clench and grind their teeth are poor candidates for porcelain veneers, as this can cause the veneers to crack or chip.