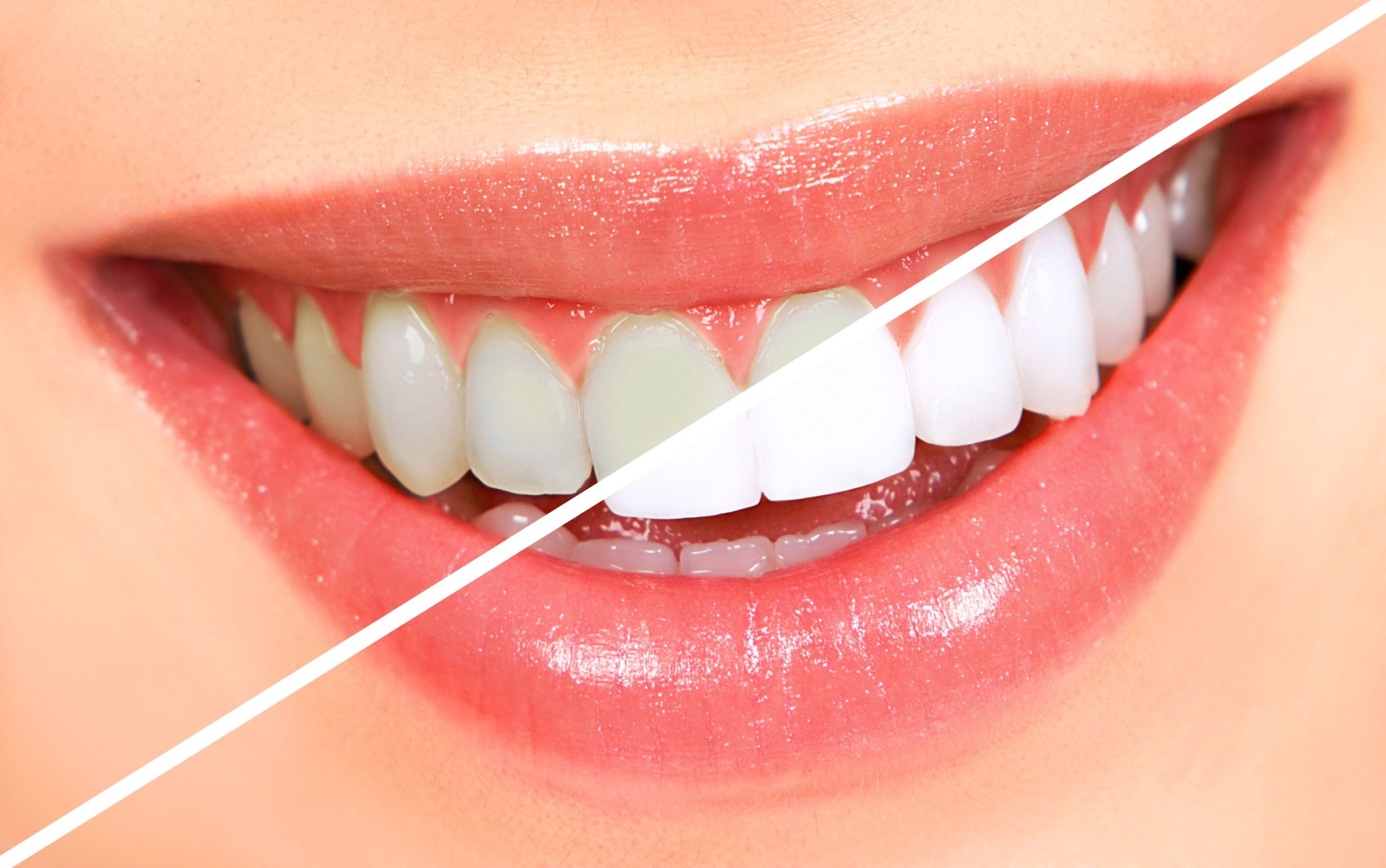
Tooth bleaching is the most common procedure in cosmetic dentistry. Bleaching of teeth is one of the most conservative and cost-effective dental treatments of discoloured teeth than aggressive methods like veneering, crowning or bonding to enhance an individual smile. It is ideal for people who have healthy and unrestored teeth and gums. Tooth whitening cannot make a complete colour change but it may lighten the existing shade and is not permanent.
Currently, bleaching agents which are used are based primarily on either hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. The peroxide oxidizing agent penetrates the porosities in the rod-like crystal structure of enamel and breaks down the stain. Yellowish teeth respond well to bleaching compared to brownish coloured teeth. Gray/purple or tetracycline stains are more difficult to lighten and may require prolonged bleaching. The effect is less likely to last as long if you smoke, eat or drink products that stain your teeth.
Bleaching can be done by two techniques – In-office bleaching and At-home bleaching. In general, both the techniques have been shown to be effective, although, the results may vary depending on such factors as the type of stains, age of the patient, the concentration of bleaching agent, treatment time and frequency. In-office bleaching contains from 15% to 43% peroxide and at-home bleaching contains from 3% to 20% peroxide.
In-Office Bleaching
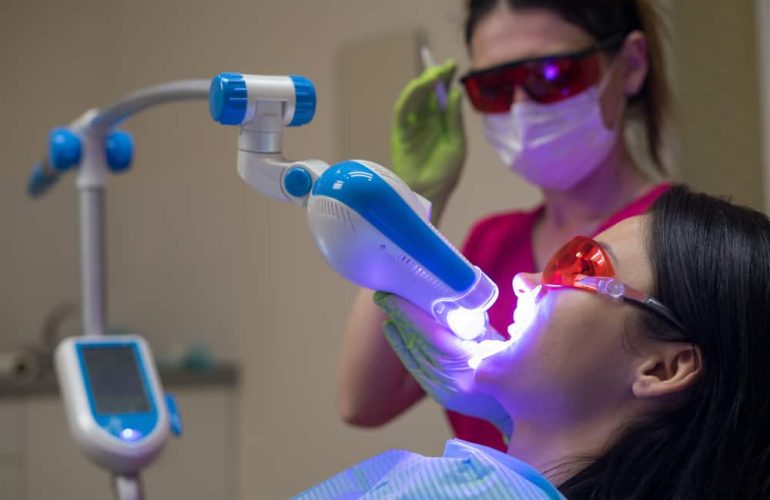
Teeth whitening is done by the dental professional. The bleaching agent is much stronger than home bleaching. Light, heat or a combination of two may be used to intensify the whitening process. Bleaching can be done in approx 30 min to 1 hr in a single visit.
Example – Zoom bleaching [most widely used bleaching process which uses the zoom advanced power chairside lamp to accelerate the bleaching process].
At-Home Bleaching
These are available over the counter or either supplied by a dental professional. Teeth whitening can be done by whitening toothpaste [mildly abrasive and does not alter the intrinsic colour of teeth], rinses, strips and gels, tray-based tooth bleaching [tray is filled with bleaching gel and placed over the teeth]. They are less expensive.
Tooth bleaching is best performed under dental professional supervision and following a pretreatment dental examination and diagnoses. Several companies have started advertising their bleaching products directly to the patients with no dentist involvement. The most appropriate bleaching treatment options may be selected according to the patient’s lifestyle, financial consideration and oral health. Success will vary when tooth discolouration is related to developmental aspects, extrinsic [smoking, diet] or intrinsic stains [tetracycline], age-related tooth changes or colour changes secondary to teeth trauma.